Shutdown Introduction
In the world of the oil and gas industry, shutdown plays a critical role in ensuring the safety, reliability, and operational efficiency of facilities. Shutdown, also known as turnaround or outage, refers to the planned and controlled suspension of operations for maintenance, inspection, repair, or modification purposes. These scheduled schedules are critical in maintaining optimal condition for equipment and infrastructure, preventing unexpected breakdowns, and extending the operational life of the assets.
Types of Shutdown
Shutdowns in the oil and gas industry can be classified into two types: Planned and Unplanned.
Planned Shutdown:
Planned shutdowns are carefully scheduled in advance to minimize disruption to ongoing operations. Planned shutdowns are also known as Turnaround. They serve several purposes, including:
A) Preventive Maintenance: Regular maintenance activities ensure longevity and peak performance of the equipment. Preventive maintenance (PM) is the regular and scheduled maintenance of equipment and assets to reduce the likelihood of equipment failure and unplanned machine downtime. Effective preventive maintenance is planned and scheduled based on real-time data insights, often using software such as a CMMS. A preventive maintenance task performed to prevent unexpected malfunctions when the equipment is still in operation.
B) Inspections: Comprehensive inspections help to proactively identify and address potential issues while ensuring the integrity of equipment and systems.
In the oil and gas industry, it is extremely important to regularly check equipment to make sure everything is safe and working well. Equipment in this industry must withstand harsh conditions such as extreme heat, strong chemicals, and frequent shaking. All this can damage the equipment, causing it to break.
Inspect frequently to catch any problems with the equipment before they become a big issue. This helps avoid costly downtime, protect the environment, and keep people safe.
There are various methods of inspection of equipment in the oil and gas industry. Some common methods are:
Visual Inspection: This is the easiest way to check the equipment. Inspectors look at equipment to see if there are any signs of damage, wear and tear, or corrosion.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): This is a set of methods that allow inspectors to test equipment without damaging it. They use techniques such as ultrasonic testing, radiography and magnetic particle testing.
Functional Testing: Inspectors test the equipment to make sure it works properly. They can check things like pressure, flow, and power.
The specific method used depends on the equipment and what needs to be checked. For example, if there is a concern about corrosion, they may use NDT methods such as ultrasonic testing or radiography.
Equipment inspection in the oil and gas industry has many benefits:
Prevents Failures: By detecting and correcting problems early, inspection helps avoid costly breakdowns and production loss.
Improve safety: Inspections catch safety issues, preventing accidents and injuries.
Increases reliability: Makes inspection operations more reliable by ensuring that equipment works well.
Meets Regulations: Many oil and gas companies are required by law to conduct regular inspections to comply with safety and environmental regulations.
C) Facility upgrades: Maintaining competitiveness and compliance with industry standards often involves upgrades or modifications during shutdowns.
D) Security Enhancements: Shutdown addresses security concerns and implements improvements for the overall safety of the facility and workforce.
Unplanned Shutdown:
Unplanned shutdowns, also known as emergency outages, are caused by unexpected equipment failures, accidents, or serious incidents. Immediate action is necessary to prevent further damage to the facility, the environment and personnel.
Importance of shutdown
Shutdowns are important for several reasons:
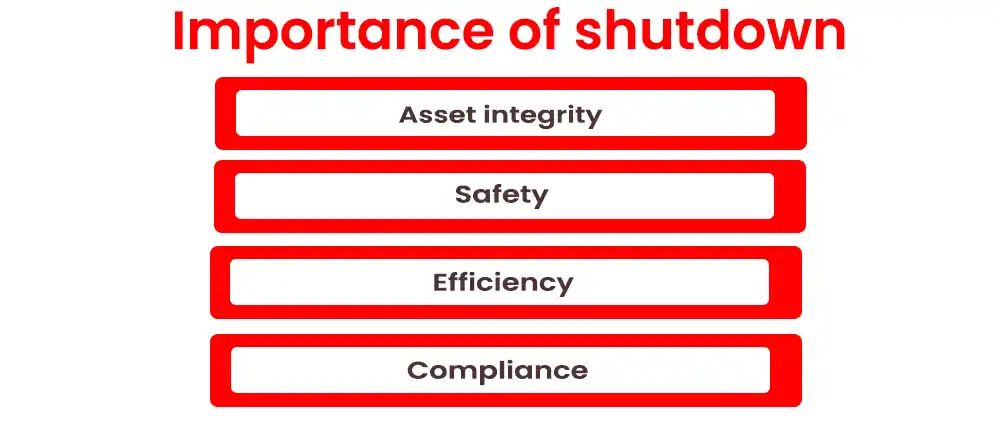
A) Asset integrity: Regular shutdowns allow operators to inspect and repair equipment, reducing the risk of costly breakdowns and accidents.
B) Safety: Safety is paramount in the oil and gas industry. Shutdowns provide an opportunity to implement safety measures and address potential threats, protecting the workforce and communities.
C) Efficiency: Optimized equipment operates more efficiently, minimizing energy consumption and maximizing production, which benefits the company’s bottom line.
D) Compliance: Shutdown facilitates compliance with regulatory standards, ensuring facilities meet environmental, health and safety requirements.
Challenges and Mitigation Strategies

While planned shutdowns offer many benefits, they also present challenges such as increased costs and potential revenue loss. To address these, industry professionals employ mitigation strategies:
A) Detailed planning: Thorough planning and coordination minimizes downtime and optimizes resources during shutdowns.
B) Advanced technology: Implementing predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring helps identify potential issues before they escalate, reducing unplanned shutdowns.
C) Efficient Execution: Timely execution of shutdown activities with a well-organized workforce ensures completion within the planned schedule.
D) Risk Assessment: Comprehensive risk assessment identifies security threats and enables the implementation of risk mitigation measures.
Difference Between Shutdown and Turnaround
Shutdowns and turnarounds are necessary events in industrial facilities to maintain safety, efficiency and overall health. Although these terms are sometimes used interchangeably, they have distinct differences. In this article, we’ll explore the dissimilarities between shutdown and turnaround, their importance, and why careful planning and implementation are important.
Shutdown:
A shutdown is a planned or unplanned event where production or operations stop temporarily. These blockages are relatively short, lasting for days or weeks. Shutdowns typically target a unit or specific area within a facility. The primary purpose of shutdown is to ensure safety, respond to emergencies, or perform minor maintenance tasks. They are less complex and expensive than turnarounds.
Turnarounds:
Turnaround, on the other hand, is a more widespread shutdown with a longer duration, sometimes lasting months or years. During a change, the entire plant or facility is affected, making it a large scale event. The main purpose of a turnaround is to perform major maintenance, repairs or upgrades. Organizations plan for change years in advance because of its complexity and cost. Despite being disruptive, changes are critical to improving safety, efficiency and the overall lifespan of a plant or facility.
Conclusions:
Shutdown is a fundamental aspect of the oil and gas industry, ensuring safety, reliability and efficiency in operations. Proactively scheduling maintenance, inspections and upgrades helps extend asset life and maintain a competitive edge. Through careful planning, efficient execution and taking advantage of advanced technologies, shutdowns become opportunities for growth, which lay the foundation for sustainable success.
Read Also
Download Free Piping PDF for Interview Preparation
What is gasket and their types
What is a valve and its types?
