In the oil and gas industry, the proper selection of pipe fitting is critical for the safe and efficient operation of piping systems. Whether it’s controlling fluid flow or ensuring leak-proof connections, pipe fittings play an essential role in maintaining the integrity of pipelines. But to achieve this, it’s important to adhere to well-established pipe fitting standards. These standards ensure the compatibility, strength, and durability of fittings in various applications.
This comprehensive guide will provide an in-depth understanding of pipe fitting standards and how they apply to professionals working in the industry. Whether you’re selecting fittings for high-pressure systems or industrial pipelines, mastering these standards is crucial for success.
What Are Pipe Fitting Standards?
Pipe fitting standards are detailed guidelines and specifications that dictate how pipe fittings should be designed, manufactured, and tested to meet specific criteria. These standards cover essential parameters such as materials, dimensions, pressure ratings, and tolerances, all of which are vital to ensure the safety and functionality of piping systems.
Adhering to these standards guarantees that the fittings used in a project meet the highest performance and safety levels. Compliance with pipe fitting standards is mandatory in industries like oil and gas, chemical processing, and construction, where any deviation can lead to catastrophic failures.
Some of the most widely recognized pipe fitting standards include:
- ASME B16.9 – Factory-made wrought steel buttwelding fittings.
- ASME B16.11 – Forged steel fittings, socket-welding, and threaded.
- API 6A – Specification for wellhead and tree equipment.
- ISO 9001 – Quality management systems standards.
- MSS SP-75 – High-strength fittings for pipeline transportation systems.
These standards ensure uniformity and compatibility across different manufacturers, reducing the risk of failure due to non-standardized components.
Key Elements of Pipe Fitting Standards
1. Material Composition
The material of pipe fittings is one of the critical factors specified by pipe fitting standards. In most industrial applications, materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, copper, and alloy steel are commonly used. The choice of material directly impacts the fitting’s resistance to corrosion, temperature, and pressure.
For instance, carbon steel fittings are preferred in high-pressure environments, while stainless steel fittings offer superior corrosion resistance, making them ideal for harsh conditions in chemical and petrochemical industries. These standards define the exact grades and specifications that should be used to ensure the right balance between durability and cost-effectiveness.
2. Pressure and Temperature Ratings
One of the most vital aspects of pipe fitting standards is the specification of pressure and temperature ratings. These ratings ensure that fittings can withstand the operational stresses they will encounter. ASME B16.5 is one such standard that specifies the pressure-temperature ratings for flanged fittings.
Fittings must be able to handle not only the normal operating pressure but also the maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP). Exceeding these ratings can lead to dangerous failures, including ruptures and leaks. Therefore, professionals must strictly adhere to these pressure and temperature ratings when selecting fittings.
3. Dimensional Standards
Dimensional accuracy is essential for ensuring the compatibility of pipe fittings. These standards dictate the exact dimensions of pipe fittings, including the inner and outer diameters, wall thickness, and end-to-end measurements. This is crucial for achieving a leak-proof connection between pipes and fittings.
For instance, the ASME B16.9 standard covers the dimensions of factory-made steel fittings, ensuring they meet the necessary tolerances for buttweld connections. These precise dimensions help eliminate issues such as misalignment, which can lead to significant operational inefficiencies and costly repairs.
4. Testing and Quality Assurance
All pipe fittings must undergo rigorous testing as per industry standards before being used in a piping system. These tests include hydrostatic testing, non-destructive testing (NDT), and mechanical testing to verify the fittings’ durability and performance under stress.
Standards like API 6A and MSS SP-75 lay out the exact testing procedures that fittings must pass, ensuring their integrity and longevity. Regular inspection and adherence to these testing protocols help reduce the risk of leaks, corrosion, and other failures that could jeopardize an entire pipeline.
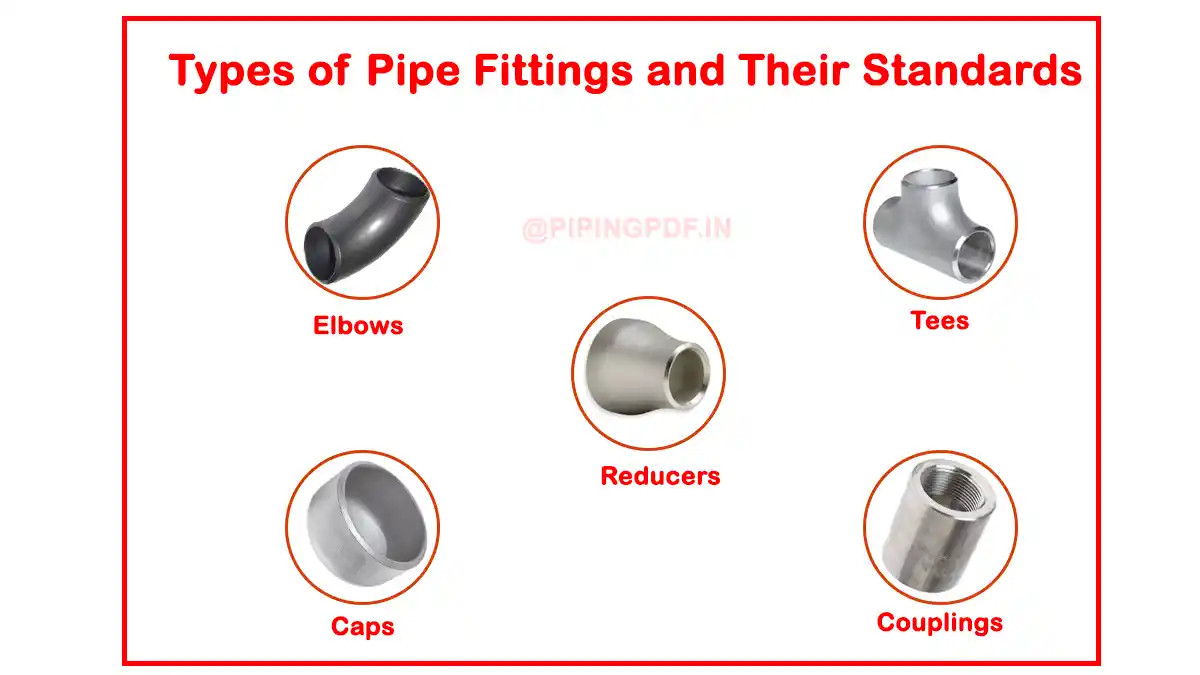
Types of Pipe Fittings and Their Standards

1. Elbows
Elbows are used to change the direction of the flow in a pipeline system. They are available in various angles, such as 90 degrees and 45 degrees. The standards for elbows are defined in ASME B16.9, ensuring that the fittings provide adequate flow control and pressure handling capabilities.
2. Tees
A tee fitting allows for branching of the pipeline, either in equal sizes or reducing configurations. The MSS SP-75 standard governs tees, providing specifications for high-strength pipeline applications, especially in oil and gas transport systems.
3. Reducers
Reducers connect pipes of different diameters, allowing for a smooth transition in flow. These are classified under ASME B16.9 and are essential for applications where reducing flow velocity is critical.
4. Caps
Pipe caps are used to close the end of a pipe, often in testing or sealing applications. Standards like ASME B16.9 specify the materials and dimensions required to ensure these caps can withstand high-pressure conditions.
5. Couplings
A coupling connects two pipes to ensure a continuous flow of fluids or gases. The ASME B16.11 standard details the manufacturing and design requirements for threaded and socket-welding couplings, ensuring they can handle the stress of high-pressure systems.
Why Following Pipe Fitting Standards Is Crucial
For professionals in industries like oil and gas, petrochemical, and construction, following pipe fitting standards is not optional. Here’s why adhering to these standards is essential:
- Safety – Ensuring that the pipe fittings meet specified standards prevents accidents and ensures operational safety.
- Cost Efficiency – Standardized fittings reduce installation errors and avoid costly repairs or replacements.
- Longevity – Using the correct materials and designs enhances the life of the piping systems, ensuring long-term reliability.
- Compliance – Many industries are regulated by local, national, and international bodies that require strict adherence to standards to maintain operational permits.
Conclusion
Understanding and applying pipe fitting standards is essential for professionals who work in the oil and gas, chemical, and construction industries. These standards ensure that the correct materials, pressure ratings, and dimensions are used, ultimately leading to safer and more efficient operations. By following these guidelines, you can guarantee that your systems will perform reliably, reducing the risk of costly failures and downtime.
Read Also
Download Free Piping PDF for Interview Preparation
Download Free Piping PDF for Interview Preparation
What is gasket and their types
What is a valve and its types?