What are the centrifugal pumps?
Centrifugal pumps are the most common type of pumps used in a variety of applications including water supply, sewage treatment, industrial processes, and irrigation. They work by converting rotational energy from an electric motor or engine into the kinetic energy of the fluid being pumped.
What are the main components of centrifugal pumps?
The main components of a centrifugal pump are:
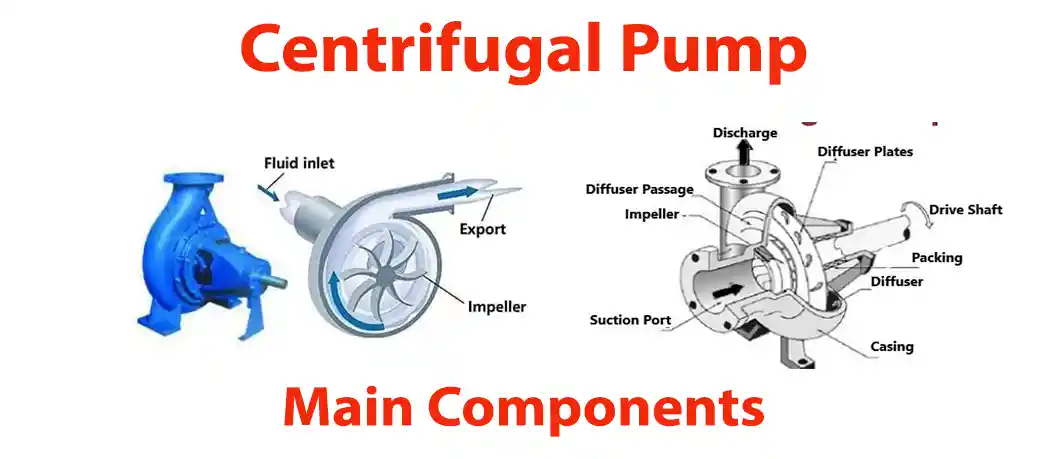
- Impeller: A rotating wheel with vanes that accelerate the fluid.
- Casing or diffuser: A housing that contains the impeller and directs the flow of the fluid.
- Shaft: A rotating shaft that connects the impeller to the motor or engine.
- Inlet and outlet ports: Openings where the fluid enters and exits the pump.
- Wear ring
- Lantern ring
- Stuffing box
- Inlet vertex
- Mechanical seal or gland packing
- Shaft sleeve
- Bearings
How centrifugal pump works?
When the pump is turned on, the impeller rotates and accelerates the fluid. The fluid is then thrown outward by centrifugal force and enters the casing. The casing is designed to slow down the fluid and convert some of its kinetic energy into pressure energy. The fluid then exits the pump through the outlet port.
How centrifugal pumps can be classified?
Centrifugal pumps can be classified according to a number of factors, including:
- Flow type: Axial, radial, or mixed flow.
- Number of stages: Single-stage or multi-stage.
- Type of volute: Single or double volute.
- Type of casing: Horizontally split, vertically split, or end-suction.
Centrifugal pumps are available in a wide range of sizes and capacities, and can be used to pump a variety of fluids, including water, sewage, chemicals, and petroleum products. They are relatively simple to operate and maintain, and are generally very efficient.
What are the advantages of centrifugal pumps?
Here are some of the advantages of using centrifugal pumps:
- They can handle a wide range of flow rates and pressures.
- They are relatively efficient and have low operating costs.
- They are simple to design and manufacture, making them relatively inexpensive.
- They are easy to operate and maintain.
What are the applications of centrifugal pumps?
Centrifugal pumps are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Water supply and distribution
- Sewage treatment
- Industrial processes, such as chemical processing, food processing, and power generation
- Irrigation
- Fire protection
- Mining
- Oil and gas production
What are the energy conversions take place in centrifugal pumps?
In centrifugal pumps hydraulic energy is being converted into kinetic energy.
What types of reducers are used at pump suction & discharge ends?
Suction side: Eccentric type & Discharge side: Concentric
What is the function of an impeller in centrifugal pumps?
It converts kinetic energy of pump into hydrodynamic energy by rotary motion
What is the function of pump casing?
Casing converts velocity head from impeller into pressure head & also guides the flow to the discharge end.
What are the types of pump casing?
Volute & diffusers are two different types of pump casing
What do you mean by volute?
A volute is a spiral-like geometry with an increasing through-flow area, reducing the velocity of the fluid and increasing the static pressure
What are the different types of volutes?
Single volute & Double volute
Write down the working principle of centrifugal pumps
In centrifugal pumps, fluid enters the impeller through inlet eye & exists along the circumference between the vanes of impeller. This impeller is connected to shaft & in turn to motor, this rotary motion of the impeller converts kinetic energy of the fluid into hydrodynamic energy.
What are the types of impellers?
Open impeller: As its name suggests, an open impeller has vanes that are open on both sides without any protective shroud. These are structurally weak.
These are used for low flow & low head applications. Generally used for pump solids or sludge. These require much NPSH.
Semi open impeller: Semi-open impellers have a back-wall shroud that adds mechanical strength to the vanes.
Closed impeller: Are very robust & require low NPSH
Impellers are also classified as single suction & Double suction
What are the rotary & stationary parts of the pumps?
Rotary parts:
Shaft
Impeller
Shaft sleeve
Bearings
Stationary Parts:
Pump casing
Gland packing or mechanical seal
Lantern ring
Why eccentric reducers are used at pump suction side?
To avoid air locking & cavitation eccentric reducers are used at suction side
What do you mean by the NPSH in pumps?
It is the net positive head required at pump suction to avoid cavitation
What do you understand by the term cavitation?
Cavitation is the formation & collapsing of vapor bubbles at pump’s suction
How the cavitation does affect the pump’s life?
Cavitation causes following impacts:
Vibrations in pump
Damage of impellers
Heavy noise
What are the factors considered for centrifugal pumps design?
Flow required
NPSH available & NPSH required
Total head
Pump efficiency
Fluid used
What are the materials used for pump casing?
Generally cast steel or cast iron are used for single stage centrifugal pumps
What are the materials used for Impellers?
Impellers are made up of cast iron, gun metal & stainless steel
What is the function of wear ring?
As the name indicates it protects the wear & tear of impeller
What do you mean by static suction head in pump?
The static suction head is the vertical distance from the center line of the pump to the free level of the liquid to be pumped.
What do you mean by static discharge head in pump?
Static discharge head is the vertical distance between the pump centerline and the point of free discharge or the surface of the liquid in the discharge tank.
What do you mean by total static head?
Total static head is the vertical distance between the free level of the source of supply and the point of free discharge or the free surface of the discharge liquid.
What do you mean by total head?
It is total dynamic discharge head plus total dynamic suction head
Note: If source water level is below the pump center line, then
Total head = Discharge head Suction lift
If source Water level is above the pump suction line, then
Total head = Discharge head-Suction head
What are the problems associated with centrifugal pumps?
Following are the common problems associated with pumps
Low discharge pressure
Low delivery
Cavitation
High vibrations
Pump seize
Over load
More suction lift
Air locking & No priming
What are the reasons for no delivery or no discharge in centrifugal pumps?
The main reasons can be as follows:
Air lock in pump suction
Suction valve closed
Low tank level
What are the reasons for low delivery?
Suction valve partially opened
Reverse rotation of pump
Low speed of pump
Suction strainer is chocked
What are the reasons for over load of pump?
More flow
High speed
Reverse rotation of pump
Pump discharge kept open to atmosphere
Internal friction in impeller & wear ring or impeller & casing
More tightened gland packing
No lubricant in bearing or bearing seized
What are the potential reasons for pump vibrations?
Overloading of pump
Reverse rotation of pump
Impeller rubbing inside the casing
Misalignment
Damaged bearing
Shaft run out
Shaft imbalance
Too much noise coming from pump inside, what does this mean?
Air lock in pump
Overloading of pump
Pump discharge line is less than actual required
Cavitation
No lubricant in bearings
What are the common mistakes done during pump installation?
Choosing poor foundation
Note: Pump foundation weight should be 3 to 4 times the pump weight
Lesser size suction pipe line
Lesser size discharge pipe line
Interchanging concentric & eccentric reducers
What are the safety protections & interlocks given for a centrifugal pumps?
Over load
Low load
High bearing vibrations
High bearing temperature
High suction DP
Source water level low
How do you increase the head & flow of pump by modifying impeller size?
By increasing the impeller diameter head & flow can be increased
By increasing the impeller width flow can be increased
What are the reasons for reduction of pump efficiency?
Operating the pump at lower capacity
Operating the pump at higher load
Throttling the discharge valve
Increase in impeller & wearing clearance
Lower suction head
High suction lift
Read Also
Download Free Piping PDF for Interview Preparation
Know more about Heat Exchanger
Download Free Piping PDF for Interview Preparation
What is gasket and their types
What is a valve and its types?

.